- Home
- Alcohol Herbal Extracts
- Alcohol-FREE Herbal Extracts
- Veterinary Herbal Extracts
- Partnership
Partnership
We are open for cooperation with all interested persons or organizations. We have plenty of partners from all around the world and are looking for a long-term cooperation with new ones. At the present time we offer the following cooperation models:

WHOLESALER
We offer up to 30% discounts for wholesalers. The exact discount amount is dependent on your order amount, quantity and size of items. Minimum order amount is $300.

PRACTITIONER
Only for licensed practitioners! Create an account as practitioner and get special exclusive promotions. This kind of account is required manual approve.

AFFILIATE PROGRAM
Do you recommend us to your friends, family, colleagues and/or clients? If so: Thanks! We really appreciate it! Join our affiliate program. It’s by far the best way to monetize your Twitter or Facebook page, blog, or website.
- Blog
- Contact Us
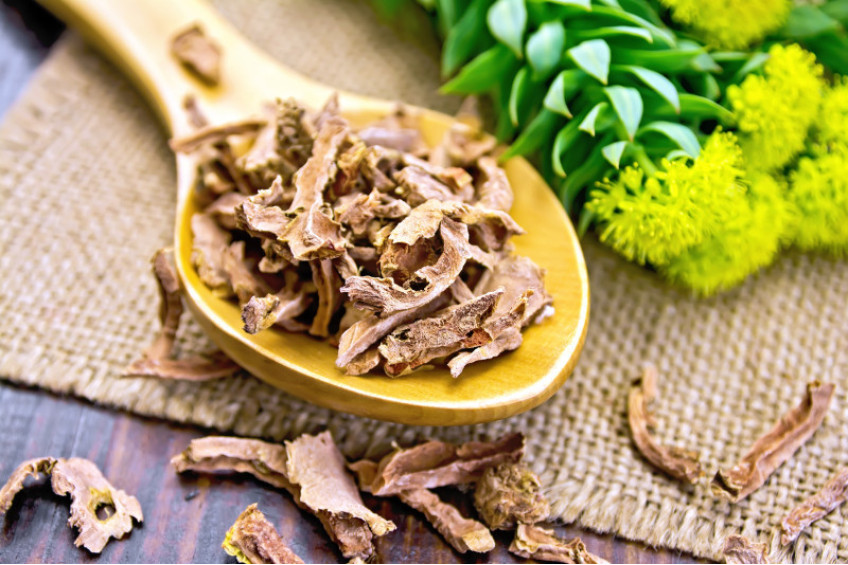

RHODIOLA, GOLDEN ROOT
Rhodiola rosea (commonly golden root, rose root, roseroot, Aaron's rod, Arctic root, king's crown, lignum rhodium, orpin rose) is a perennial flowering plant in the family Crassulaceae. It grows naturally in wild Arctic regions of Europe (including Britain), Asia, and North America and can be propagated as a groundcover.
Rhodiola rosea is from 5 to 40 centimetres (2.0 to 15.7 in) tall, fleshy, and has several stems growing from a short, scaly rootstock. Flowers have 4 sepals and 4 petals, yellow to greenish yellow in color sometimes tipped with red, about 1 to 3.5 millimetres (0.039 to 0.138 in) long, and blooming in summer. Several shoots growing from the same thick root may reach 5 to 35 centimetres (2.0 to 13.8 in) in height. R. rosea is dioecious – having separate female and male plants.
An Arctic plant that thrives in extreme environments, rhodiola’s rose-colored roots have pronounced medicinal activity, enhancing the ability of the body to deal with stresses of all kinds. An adaptogen, similar to ginseng, rhodiola also acts on the central nervous system, supporting memory and concentration under conditions of stress, and helping to relieve nervous exhaustion. Rhodiola root is most commonly taken to improve mental and physical performance.
Habitat and Cultivation
Rhodiola is indigenous to mountainous and Arctic regions of the northern hemisphere, including Canada, Scotland, Scandinavia, Russia, and Alaska. Rhodiola is still mostly collected from the wild, threatening its long-term survival in some regions, though it is now cultivated in Canada, Norway, and Finland.
Related Species the Central Asian R. quadrifida is used in Mongolia to enhance strength and vigor. R. crenulata and R. rosea are used in Chinese medicine, though across China many different species of Rhodiola are used to alleviate fatigue and protect against the cold. Chinese research into R. crenulata indicates that this species aids endurance and has a protective activity against radiation.
Key Constituents:
- Phenylpropanoids (rosavins—occuring only in Rhodiola rosea)
- Salidroside
- Flavonoids
- Monoterpenes (including rosiridin)
- Triterpenes
Research
- Adaptogen
Rhodiola is an unusual adaptogen that combines the ability to promote physical and mental endurance with anti-inflammatory activity. Though large-scale clinical trials are lacking, research shows that rhodiola root increases the capacity to resist physical and mental fatigue.
- Clinical trials in a 2000
Armenian clinical trial, young healthy hospital doctors working night shifts were given a rhodiola extract. After 2 weeks, those taking the extract showed significantly fewer signs of mental fatigue, including better levels of concentration and short-term memory, than those taking a placebo.
Traditional & Current Uses
- Key traditional uses
In Europe and Asia, the central core of rhodiola’s use in traditional medicine has always been its power to increase endurance and work rate, and the capacity to cope with high altitude and winter cold. Rhodiola is now most commonly taken to improve mental and physical performance and to protect against the harmful effects of ongoing stress.
- Rhodiola became an official medicine in 1969, being recommended for a wide range of health problems, not only as an adaptogen, but for psychiatric and neurological problems.
Source: Encyclopedia of Herbal Medicine by Andrew Chevallier, FNIMH
VALERIAN
Valeriana, or Valeriana officinal, belongs to the family Valerianaceae. It is known as a perennial plant that grows in Europe, North America and Asia although its motherland is known to be England. Yo..
WILD LETTUCE
This plant belongs to the family Asteraceae. It is a biennial herbaceous plant, can reach a height up to 150 cm. It has a smooth, bare, slightly bristly stem. The flowers are yellow in color, collecte..
Get exclusive deals you will not find anywhere else straight to your inbox!
Subscribe / UnsubscribeCookies policy
 We use cookies and similar technologies that are necessary to operate the website.
You can consent to our use of cookies by clicking "Accept..."
We use cookies and similar technologies that are necessary to operate the website.
You can consent to our use of cookies by clicking "Accept..."
Get exclusive deals you will not find anywhere else straight to your inbox!
Subscribe / UnsubscribeWe meticulously produce our extracts according to precise standards where each herb is extracted according to the distinct characteristic of each plant! Hawaii Pharm LLC offers the biggest choice of liquid herbal extracts in the World!

Hawaii Pharm LLC - Nature Heals. Highest Quality Herbal Products Since 2008.